Solaris fault administration using fmadm command
In this article we will study how we can use the fmadm command to get the list of faulty components along with the detailed information about the fault. Before starting this article we should have a command console open and then we can proceed with using the fmadm command. The most basic form of using fmadm command is using its faulty subcommand as follow
|
|
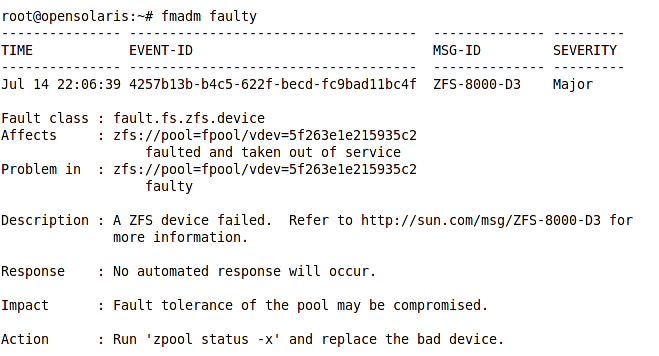
Starting from top we have:
- Identification record: This record consisting of the timestamp, a unique event ID, a message Id letting us know which knowledge repository article we can refer to for learning more about the problem and troubleshooting and finally the fault severity which can be Minor or Major.
- Fault Class: This field allows us to know what is the device hierarchy causing this fault
- Affects: tells us which component of our system is affected and how. In this instance some devices are missing and therefore the fault manager takes the Zpool out of service.
- Problem in: shows more details about the problem root. In this case the device id.
- Description: this field refer us to the a knowledge base article discussing this type of faults
- Response: Shows what action(s) were executed by fault manager to repair the problem.
- Impact: describe the effect of the fault on the overall system stability and the component itself
- Action: a quick tip on the next step administrator should follow to shoot the problem. This step is fully described in the knowledge base article we were referred in the description field.
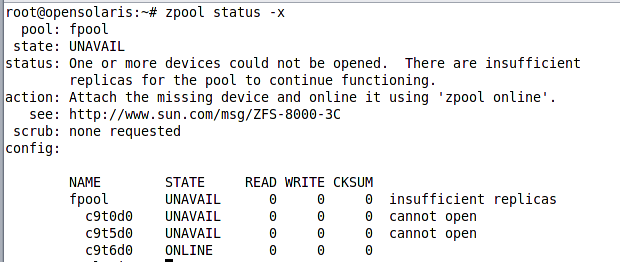
Following figure shows the output for proceeding with the suggested action.
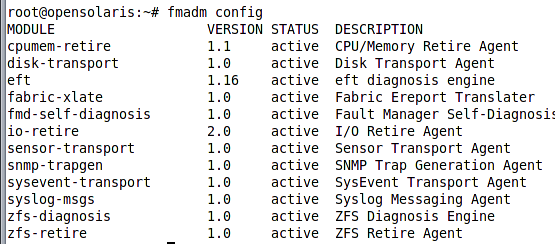
As we can see the same article we were referred to, is mentioned here again. We can see that two of the three devices have failed and fpool had no replica for each of those failed device to replace them automatically. If we had a mirrored pool and one of the three devices were out of service, the system could automatically take corrective actions and replace continue working in a degraded status until we replace the faulty device. The fault management framework is a plug-able framework consisting of diagnosis engines and subsystem agents. Agents and diagnosis engine contains the logic for assessing the problem, performing corrective actions if possible and filing the relevant fault record into the fault database. To see a list of agents and engines plugged into the fault management framework we can use config subcommand of the fmadm command. Following figure shows the output for this command.
As we can see in the figure, there are two engines deployed with OpenSolaris, eft and the zfs-diagnosis. The eft, standing for Eversholt Fault Diagnosis Language, is responsible for assessing and analyzing hardware faults while the zfs-diagnosis is a ZFS specific engine which analyzes and diagnoses ZFS problems.
The fmadm is a powerful utility we which can perform much more than what we discussed. Here we can see few other tasks we can perform using the fmadm.
We can use the repaired subcommand of the fmadm utility to notify the FMD about a fault being repaired so it changes the component status and allows it to get enabled and utilized.
For example to notify the FMD about repairing the missing underlying device of the ZFS pool we can use the following command.
|
|
|
|
|
|