Managing Logical network interfaces in Solaris
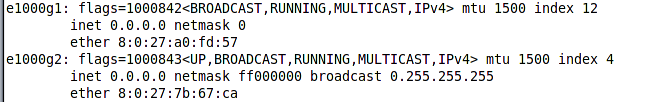
Like other operating system we can assign multiple IP address to a network interface. This secondary address are called logical interfaces and we can use them to make one machine with one single network interface own multiple IP addresses for different purposes. We may need to assign multiple IP address to an interface to make it available to both internal and external networks or for testing purposes. We should have one network interface configured in our system in order to create additional logical interfaces. We are going to add a logical interface to e1000g1 interface with a 10.0.2.24 as its static IP address. Before doing so let’s see what network interface we have using the ifconfig command.
Now to add the logical interface we only need to execute the following command:
|
|
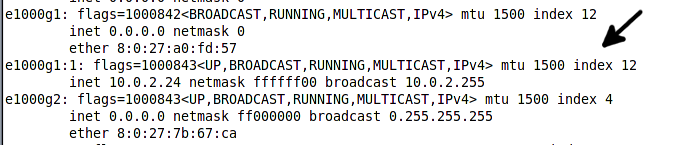
- Create a logical interface named e1000g1:1. The naming schema for logical interfaces conforms with interface_name:logical_interface_number which the number element can be from 1 to 4096.
- Assign 10.0.2.24/24 as its IP address, net mask and broadcast address.
Now if we invoke ifconfing -a command the output should contain the logical interface status as well. The following figure shows a fragment of ifconfig -a command.
Operating system does not retain this configuration over a system reboot and to make the configuration persistent we need to make some changes in the interface configuration file. For example to make the configuration we applied in this recipe persistent the content of /etc/opensolaris.e1000g1 should something similar to the following snippet.
|
|
|
|